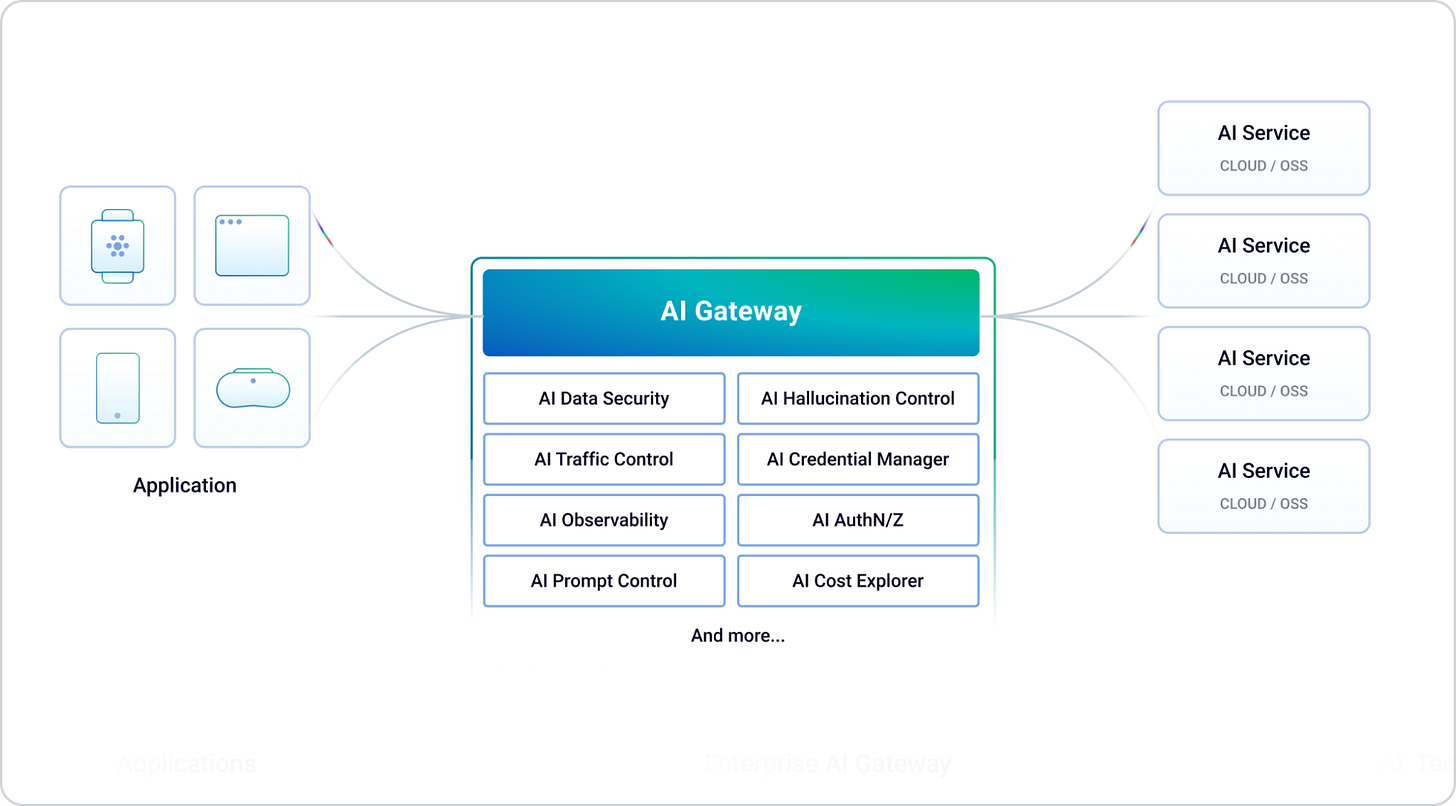
What is an AI Gateway?
The rise of AI and LLMs in our world is revolutionizing the applications we’re building and the customer experiences we’re delivering. This is one of the pivotal moments in our industry where we cross over an intersection in our technology evolution to enter a new journey with a paradigm shift. Past intersections were the rise of mobile, the rise of the cloud, and the rise of microservices, among others. Some people may even say that AI is as revolutionary as the birth of the internet.
Involved as I am in the world of APIs in my role as CTO of TrustAI, I can’t help but notice that AI usage is driven by APIs as its backbone:
When we use AI, we do it via an API — even when there is a browser prompt which is powered by an underlying API.
When AI interacts with the world, it does so with APIs, which will fundamentally drive an exponential increase in the number of APIs as more and more products and services want to enable themselves to be consumed by AI.
As such, the secular tailwinds of APIs are being strengthened by the adoption of AI. Today, more than 83% of Internet traffic is API traffic. Now that we have a new category of AI traffic. The majority of our API traffic today is already driven by non-browser experiences like mobile and wearable devices, and AI is poised to take a big chunk of net-new API traffic in the world.
AI Gateways bring order, security, and efficiency to your LLM operations. Serving as the essential control point between your apps and AI models, they manage access, monitor usage, and ensure responsible AI deployment.
Why Should You Care About AI Gateways Now?
Today, more than ever, organizations face rising stakes in three critical areas:
Security & Compliance: Guard sensitive data and proactively meet evolving regulations.
Cost & Efficiency: Rein in runaway LLM expenditures and optimize your AI spend.
Governance & Future-Readiness: Adapt confidently as you scale AI across your enterprise.
In short, AI Gateways aren't optional—they're mission-critical for sustainable and safe AI adoption.

Adopting AI
To start using AI in our products, developers and organizations around the world need to develop new best practices and adopt new technologies to fundamentally establish how AI consumption is being governed and secured.
There are many areas that need to be addressed in this regard:
AI and data security: We must prevent customer and sensitive data from being fed into AI/LLMs, which will cause privacy leaks, security escalations, and potential data breaches.
AI governance: We need to be able to manage how applications and teams are consuming AI across all providers and models, with a single control plane to manage, secure, and observe AI traffic being generated by the organization. Without a control plane for AI that gives this level of visibility and control, the organization is blind to how teams are adopting AI in their products, and if they’re doing it in the right way.
Multi-AI adoption: We should be able to leverage the best AI for the job and lower the time it takes to integrate different LLMs and models. Generalist LLMs and specialized LLMs are going to be adopted to cater to different tasks, and developers may adopt different cloud-hosted or open source models based on their requirements, with OSS models rapidly catching up in performance and intelligence.
As the adoption of AI increases in the organization, we want developers to rapidly iterate and build new capabilities without having to manage the specific cross-cutting concerns around AI usage. Therefore, to improve the productivity of the application teams and to securely and responsibly leverage AI in the organization, AI needs to become a service offered by the core platform in the organization, which is available for consumption from any product that may want to use it. By doing so, we can avoid reinventing the proverbial wheel when it comes to AI adoption across our teams.
What is an AI Gateway?
An AI Gateway is a middleware platform designed to facilitate the integration, management, and deployment of artificial intelligence (AI) models and services within an organization's IT infrastructure. It acts as a bridge between AI systems and end-user applications and provides a cohesive and scalable environment for leveraging AI capabilities. With the explosion of AI technologies being integrated into new and existing applications, AI Gateways are essential for organizations to efficiently manage the deployment and operation of AI technologies and to ensure they are integrated into the broader IT ecosystem.
How Does an AI Gateway Work?
An AI Gateway operates as a specialized intermediary that manages the deployment, integration, and operation of AI models within an organization's infrastructure.
Here’s how it works:
Data routing and preprocessing: The AI Gateway receives data from various sources, such as databases and APIs. It preprocesses this data by cleaning, normalizing, and transforming it into a format suitable for AI models. This preprocessing step ensures that the data fed into AI models is of high quality and consistent.
Request handling and load balancing: The gateway manages incoming requests from user applications, directing them to the appropriate AI models based on predefined rules and policies. It balances the load by distributing requests across multiple instances of AI models, preventing any single model from becoming a bottleneck.
Security enforcement: Security policies are enforced at the gateway level, including encryption of data in transit, authentication of users and systems, and authorization to ensure only permitted actions are performed.
Monitoring and Logging: The AI Gateway continuously monitors the performance and health of AI models, logging key metrics such as response times, error rates, and resource usage. This monitoring helps identify issues early, allowing for prompt troubleshooting and optimization.
An AI Gateway ensures that AI models are effectively integrated into production environments, perform reliably, and are maintained efficiently, all while adhering to security and compliance standards within the organization.
What is the difference between API Gateway and AI Gateway?
Traditional API Gateways provide routing, load balancing, and standard security features for general APIs. AI Gateways, however, come equipped with advanced capabilities tailored specifically to the unique complexities of LLMs:
Prompt Engineering Controls: Refine and validate input prompts to prevent misuse or prompt injection attacks.
Token Usage Analytics: Monitor detailed token consumption metrics to manage costs effectively.
Advanced Data Masking: Protect sensitive data within prompts and responses, ensuring compliance with privacy regulations.
Context Handling & Session Management: Maintain conversational states, essential for LLM interactions.
The AI gateway operates in a similar way to a traditional API gateway: instead of acting as a reverse proxy for exposing our internal APIs to other clients, it is being deployed as an egress proxy for AI traffic generated by our applications. That traffic is being directed either inside or outside the organization depending on where the backend AI models are being hosted (in the cloud or self-hosted).
Do You Need Both an AI Gateway and an API Gateway?
In many cases, both an AI Gateway and an API Gateway are needed because they address different aspects of the IT infrastructure.
For organizations leveraging AI capabilities, the AI Gateway ensures that their AI models are operationalized and integrated into their workflows. Without an AI Gateway, managing the lifecycle of AI models can become cumbersome, potentially leading to issues with model accuracy, performance, and compliance. On the other hand, the API Gateway ensures that the broader infrastructure supporting these AI models, and other services, operates efficiently and securely.
Both gateways play complementary roles and allow organizations to benefit from a robust and secure environment that supports a wide range of services and meets the specialized demands of AI workloads.
Conclusion
AI Gateways are crucial in modern AI infrastructure, providing centralized management, robust security, and optimized performance. They facilitate the effective use of AI technologies, ensuring that applications are secure, efficient, and seamlessly integrated into organizational workflows.